Price/Cost table
| Type | Price/Cost $SGD |
| Periapical X-ray | $80 - $120 |
| Panoramic X-ray | $80 - $120 |
| Intraoral X-rays | $100 - $250 |
| Occlusal/palatal X-ray | $30 - $50 |
Dental X-Ray: Everything You Should Know About It
A dental X-ray is an effective diagnostic tool that helps to examine your oral health better. In most cases, it is used to visualise hard tissues like bones and joints but sometimes it is employed to capture soft tissues too. Some problems with the teeth are located deep inside the gums and structures and practically invisible to the naked eye. An X-ray can detect the likes of tooth decay, cavities, jaw problems, gingivitis, and more.
As a patient, it is normal for you to have plenty of questions and concerns about this diagnostic tool. Hopefully, the following article will help you learn more about the method and make you feel more comfortable getting a scan. Below, you will find the kind of information you are interested in.
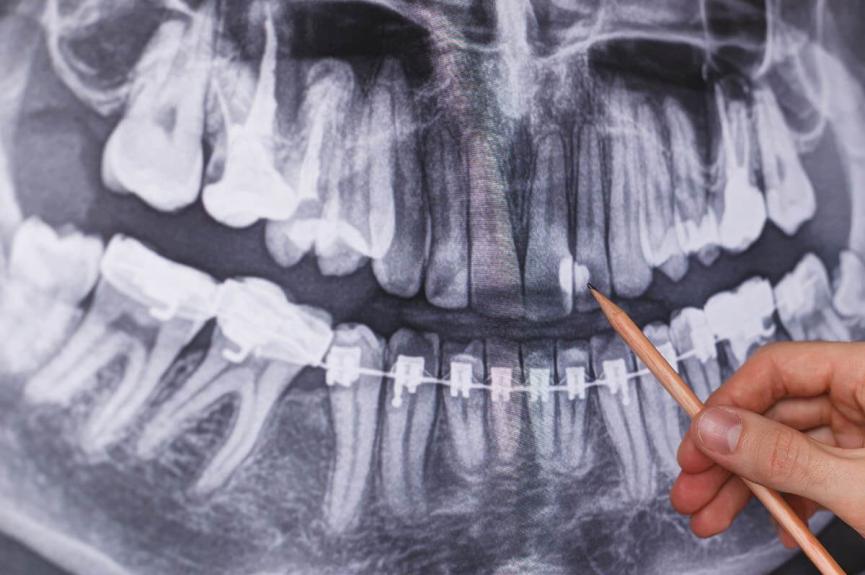
Dental X-ray vs Background Radiation
Before we embark on this, let’s talk about something that goes by the name background radiation. Naturally, we are surrounded by radiation, so to say. It’s coming from radioactive elements around us like the sunlight, cosmic rays, and soil, and we even have such elements in our bones and blood (Radium 226, Carbon 14, Potassium 40).
And then we have X-rays. This is a kind of ionizing electromagnetic radiation that is widely used in the medical field for screening and treatment purposes. It passes through the body without having to make an incision and is impossible to see with the naked eye.
The way it works is by creating images of inside structures in your body such as chest, neck, GI tract, entire mouth, and calf, among other things. It comes in big free-standing machines that emit radio and light waves. Once aimed at the part of the body that has to be examined, it quickly delivers small doses of radiation to the area and then creates an image on a special detector or photographic X-ray film.
When X-ray images come in the form of digital files (produced by more advanced digital X-rays or digital radiography), they can be accessed at any time for diagnosis, regardless of the time and place. They are stored electronically. This also enables the specialists, dentists including, to change the brightness and contrast of the image so they can see some parts better. The advances of digital x-rays are immense in recent years1 and bring many advantages2, one of the main ones being the reduced radiation exposure3.
Now, you may think that X-rays are mostly employed to detect fractures in the bones, but they have plenty of other uses and are of great help in various medical fields. To illustrate this, X-rays can spot breast cancer, pneumonia, (non)cancerous bone tumours, other lung problems, swallowing problems (dysphagia), dental abscesses, and other tooth problems. As you know, the latter issue are handled by a dentist or another dentistry specialist. When
Dental X-ray Techniques
Here are the basic types of X-ray you may encounter at the dentist’s office:
- Intraoral X-rays vs extraoral X-rays: the former means that the X-ray film is inside the mouth while the latter has it the other way around. The most usual type of X-ray is intraoral X-ray.
- Occlusal/ palatal X-ray. This one detects cysts, growths, jaw fractures, and teeth that still haven’t come out. It may be able to diagnose a cleft palate as well.
- Bitewing. It can help spot periodontal disease, tooth decay, and cavities, as well as examine the height of the bone that your teeth are holding on to.
- Periapical dental X-ray. Periapical X-rays show teeth from the bones beneath it to the crown. It can aid in a root canal treatment plan or other procedures, as it covers a specific area of the mouth.
- Panoramic X-ray examination. This one attempts to capture all your teeth, both upper and lower. It helps dentists plan for dental implants, examine jaw problems, and check on wisdom teeth, among other things. The main difference from the other types of dental X-ray is that the machine spins around your head.
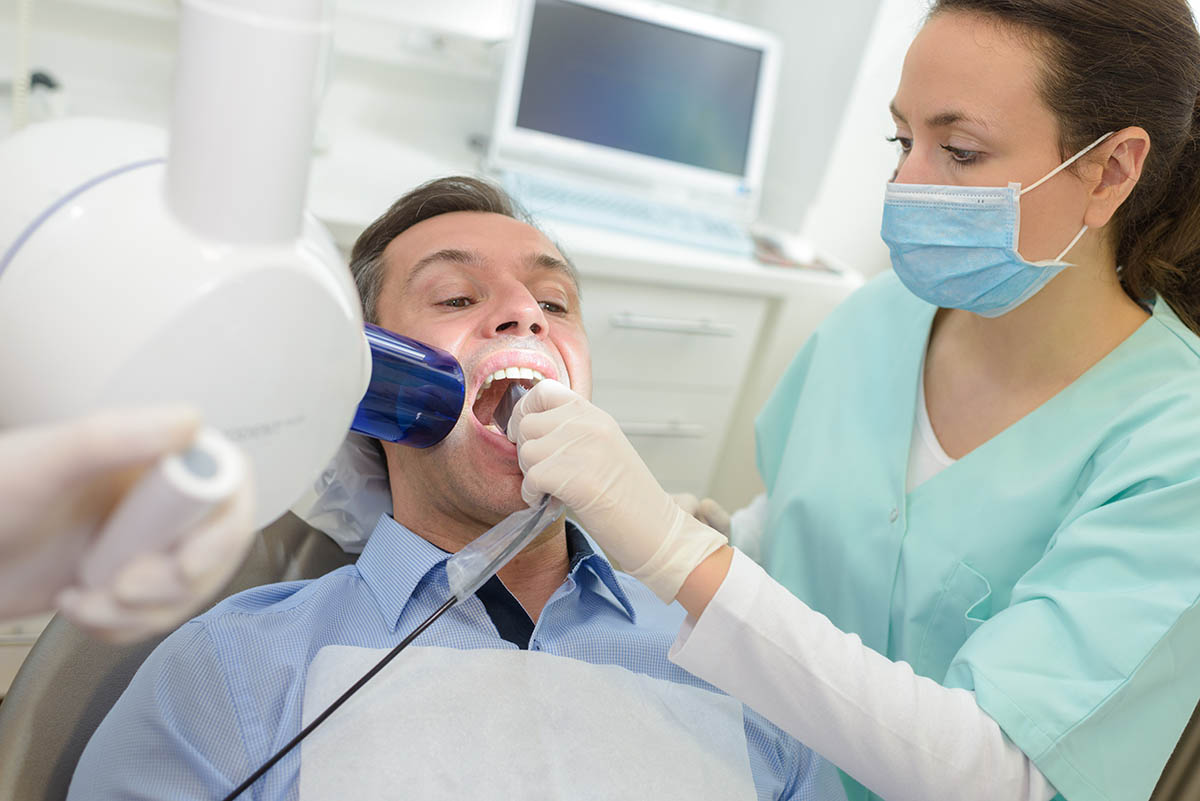
What is the Typical Dental X-ray Process Like?
A dental X-ray procedure does not presuppose any preparation. You will be taken to the radiology department and ushered into an office or dark room where the professional X-ray equipment is kept. The technician that is in charge will guide you through the process, just follow their instructions. You will stand still in front of a plate. Remove your earrings, metal objects, eyeglasses, and other jewellery from the area that will be scanned beforehand.
If you need a bitewing X-ray, you will have to bite down a piece of paper. For panoramic images, the radiologist/dentist may cover your neck and lower body with a thyroid collar and lead apron whilst the machine is moving around your head and taking pictures of your mouth from different angles. A few seconds later, everything will be over and you will be asked to wait outside for the X-ray picture/radiographs or come back another day to get them. There is no pain or discomfort during the screening. In some cases, the dentist will receive the results first.
How Much Does an X-ray Cost in Singapore?
Dental X-ray charges differ in size for each dental clinic, so here is a ballpark figure to go by when setting up your budget:
- Periapical X-ray - $80 – $120
- Panoramic X-ray - $80 – $120
- Intraoral X-rays - $100-$250
- Occlusal/palatal X-ray - $30-$50
Depending on where you get the job done, the dental X-ray cost (Singapore) will be amplified. Each laboratory has different rates and a patient has to investigate those in advance. The number of radiographic images you need to take will also add to the price. Do ask the staff for the overall cost prior to your dental visit so that you come prepared.
What is Referred to as Dental X-ray Exposure Time?
The exposure to radiation pivots on several factors including the sensitivity of the tissue, scan duration (exposure time), patient’s size, and the tooth X-ray equipment itself. (There are different dental X-ray machine types).
Scan duration varies anywhere from 0.125 seconds to 0.32 seconds or more. This is the time that it takes for the device to create the images. And it translates into a different amount of millisieverts (mSv) that a patent will receive during the screening process.
For example, a panoramic dental radiograph typically exposes you to 0.007 mSv, roughly speaking, which is the equivalent of two days of natural background radiation. The amount can reach up to 0.09 mSv. Set side by side, the effective doses of chest X-rays and intraoral dental X-ray are higher - around 1 mSv and 1-8 mSv respectively. For members of the general public, the accepted limit of radiation exposure is 1mSv per year.
Also, digital X-rays can produce up 80% less radiation than traditional devices. However, due to this fact often clinics would administer more x-ray imaging to patients which could negate this benefit of digital radiography4.
In comparison, computed tomography (CT) exposes a patient to bigger doses of radiation, which may equal 5-8 years of background exposure. For instance, a CT scan of the abdomen is equivalent to 8 mSv, whereas as CT of the chest is around 7 mSv.
In a word, a teeth Xray examination has less radiation than a CT scan. So, next time your dentist suggests going through with the screening, don't be afraid to have it performed on you. It will be crucial for your treatment. Of course, you should do it only if you need it, not at random. Patients who are asked to undergo X-rays every six months should definitely think about going to another specialist.
Teeth X-ray Side Effects
X-ray teeth imaging is not likely to cause any side effects. It is a pain-free procedure. If barium enema is added to the testing, it can make you feel sick and bloated or give you a mild headache. However, barium enema is used for radiographs on the bowel rather than the teeth and is not related to dental imaging.
Are Dental X-rays Safe?
Yes, but there are a few precautions. As evident from the numbers above, dental X-ray teeth screening is relatively safe5, as the radiation dose is smaller than one day of background radiation. Even though panoramic images seem to be on the high end of that range, they will not skyrocket your radiation exposure either. In most cases, the dose you get from a single panoramic image will be equal to that of a couple of days’ background radiation.
That said, we feel obliged to discuss this matter further so you know all the facts. A completely safe exposure to radiography is practically non-existent, even when it comes to small areas like your mouth. Let’s talk about your radiation risk in more detail.
Dental X-ray radiation risk
What is meant by the term radiation dose is the amount of energy your body will absorb when exposed to X-rays. However, the best way to convey how much radiation a patient actually gets is in terms of effective dose. This can be very confusing, so we are not going to go into the technicalities here. The only thing you need to remember is that it measures how much radiation different tissues and organs will face. Organs are known to have a varying sensitivity to radiation: some absorb more, others less.
Another striking fact is that radiation from medical imaging has a cumulative effect which is why it is crucial to undergo X-ray on teeth only when it’s 100% needed. Find a dentist with a similar approach to the matter.
How often should I get dental X-rays then?
That would depend on your history of dental issues. If you have an ongoing problem or tend to get cavities all the time despite your best effort to have good oral health, a dental hygienist may order digital X-rays every six to 18 months until the problem declines. But if you have to deal with minor problems from time to time, there is no need to undergo the exam so frequently.
If the dentist is following the dental radiography guidelines, you will be urged to take it every three or five years just to make sure your teeth are in good condition. (i.e. The specialist won’t put you through unnecessary scanning if they follow the guidelines.) Whether you will need a specific area screened or the entire mouth, the technician will be the judge of that.
So, if you are asking yourself: “How many dental X-rays are safe per year?”, the answer would be: one every three or so years.
What does Research say on the Dangers of Panoramic Dental X-rays?
There are studies on the health effects or dental X-rays and panoramic images but they are not definitive. Some correlation was found between overall health and dental X-rays but so far no clear evidence has been offered on the matter. Specifically, there have been talks about elevated cancer risk6 in the neck and head regions, such as meningioma, parotid gland tumour, salivary glands cancer, and brain cancer. Long-term radiation exposure from X-rays could have some health effects and this is especially true for radiologists. More research needs to be done with regard to how it affects patients.
Are Panoramic Dental X-rays Necessary?
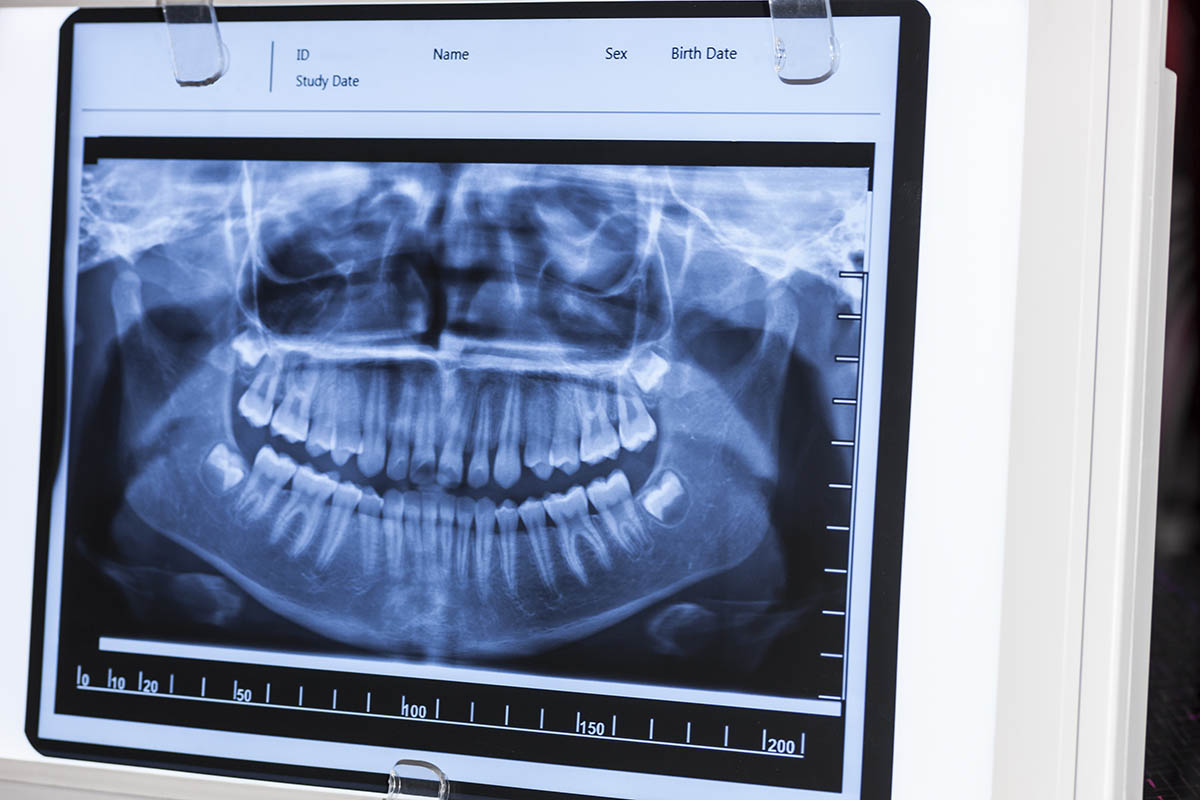
Having read the above section, you are probably wondering whether you should do panoramic X-rays at all. The answer is: yes. The benefits of X-rays far outweigh their risk factors. A dentist may order such a test on different occasions. A panoramic image takes a peek at your entire mouth (both anterior and posterior teeth), giving insights into the current status of your bone structure (bone loss and bone density), molars, wisdom teeth, and jaw.
On that note, it can help diagnose oral tumours, sinusitis, gum disease, periodontal disease, impacted teeth, TMJ disorders, as well as emerging teeth. This shortens the patient journey from the detection of problem to treatment options.
A wisdom teeth Xray, or panoramic X-ray, is the preferred method for scanning wisdom teeth. This is the only form of electromagnetic radiation that can cover the entire jaw.
Can I Do an X-ray when Pregnant?
Dental X-ray and pregnancy don’t go hand in hand and should be used only as a last resortt7. Speak with your dental care provider to see if it is absolutely necessary to have the test done. Do mention that you are pregnant. It is understandable why you would be concerned. That’s why you should have a word with the specialist beforehand to let them assess your condition and make the best decision.
Now, given the area of exposure, dental radiographs only affect the upper portion of the body - head and neck - while the pelvic floor and abdomen remain intact. This means that even if you do choose to proceed with the exam, it will not hurt your unborn baby8. Besides, the radiation dose is the lowest possible.
However, sometimes the cone beam of the X-rays may accidentally land on the abdomen. There is no way to predict that. For this reason, the teeth Xray technician might want to cover your lower part of the body with a lead apron/shield to protect your vital organs and the foetus from absorbing radiation.
Another aspect to take into account is that although there is no risk of birth defects or miscarriage associated with the screening method, a possibility exists of the baby developing cancer in early childhood. In other words, your best bet is to stay away from teeth Xray during pregnancy. Any dentist will tell you so too.
What about Child Dental X-ray?
Children can receive X-rays only when it’s medically necessary and recommended by the kids dentist but the exposure to an X-ray beam should be limited9. In general, kids are more sensitive to radiation, so special paediatric methods have to be used during the screening. An infant dental X-ray machine guarantees the lowest dose of radiation possible with no further complications. Ask your dentist for more information.
Can I Refuse a Dental X-ray?
As a patient, you have the right to refuse treatment or a diagnostic test, including dental radiography on your mouth. Make sure to consult a professional and trustworthy dentist or dental hygienist with experience and don’t be afraid to seek a second opinion. However, if an x-ray is prescribed by a specialist, refusing it may leave serious issues undetected10.
- 1. https://pubs.rsna.org/doi/full/10.1148/rg.273065075
- 2. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18539866/
- 3. https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/digital-radi...
- 4. https://www.iaea.org/resources/rpop/health-professionals/radiology/radio...
- 5. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6341170/
- 6. https://www.health.harvard.edu/cancer/radiation-risk-from-medical-imaging
- 7. https://americanpregnancy.org/is-it-safe/x-rays-during-pregnancy-1189
- 8. https://www.nhs.uk/common-health-questions/pregnancy/can-i-have-an-x-ray...
- 9. https://www.aapd.org/globalassets/media/publications/archives/nowak-03-s...
- 10. https://www.hhs.gov/answers/public-health-and-safety/how-can-i-reduce-ra...







